General Info
| Host: | Rabbit |
| Applications: | WB/IHC/IF/ELISA |
| Reactivity: | Human/Mouse/Rat |
| Note: | STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
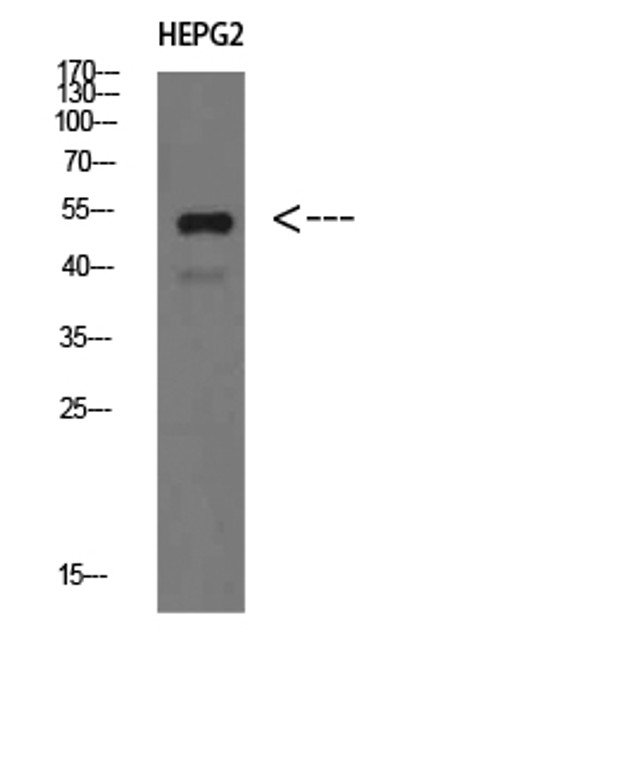
| Short Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody anti-Immunoglobulin heavy constant mu (391-440 aa) is suitable for use in Western Blot, Immunohistochemistry, Immunofluorescence and ELISA research applications. |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Conjugation: | Unconjugated |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Formulation: | Liquid in PBS containing 50% Glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% Sodium Azide. |
| Purification: | The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen. |
| Concentration: | 1 mg/mL |
| Dilution Range: | IHC-P 100-300WB 1:500-2000ELISA 1:10000-20000IF 1:50-200 |
| Storage Instruction: | Store at-20°C for up to 1 year from the date of receipt, and avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
Information
| Gene Symbol: | IGHM |
| Uniprot ID: | IGHM_HUMAN |
| Immunogen Region: | 391-440 aa |
| Specificity: | IgM Chain C Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of IgM Chain C |
| Immunogen: | Synthesized peptide derived from IgM Chain C at the amino acid range 391-440 |
Description
| Function | Constant region of immunoglobulin heavy chains. Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, are membrane-bound or secreted glycoproteins produced by B lymphocytes. In the recognition phase of humoral immunity, the membrane-bound immunoglobulins serve as receptors which, upon binding of a specific antigen, trigger the clonal expansion and differentiation of B lymphocytes into immunoglobulins-secreting plasma cells. Secreted immunoglobulins mediate the effector phase of humoral immunity, which results in the elimination of bound antigens. The antigen binding site is formed by the variable domain of one heavy chain, together with that of its associated light chain. Thus, each immunoglobulin has two antigen binding sites with remarkable affinity for a particular antigen. The variable domains are assembled by a process called V-(D)-J rearrangement and can then be subjected to somatic hypermutations which, after exposure to antigen and selection, allow affinity maturation for a particular antigen. Isoform 1: Constant region of secreted IgM (sIgM), also known as the Fc region of IgM antibody. Able to multimerize, forms high order polymers, mainly pentamers and occasionally hexamers, providing for multivalency and high avidity recognition of antigens. Natural sIgM are polyreactive and recognize conserved self- and pathogen-derived structures, whereas immune sIgM are secreted only upon exposure to pathogens and are antigen-specific. Both natural and immune sIgM are required for an efficient humoral immune response to infection. Mediates sIgM effector functions mostly via Fc receptors and the complement system. On lymphoid cells binds high-affinity Fc receptor FCMR and promotes induction of an efficient neutralizing IgG response while maintaining tolerance to self-antigens. Recruits C1q complement component to initiate the classical complement pathway, facilitating the recognition and neutralization of pathogens by the host. Together with C1q and mannose-binding lectin promotes the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages, ensuring the clearance of potential autoimmune epitopes from tissues. Involved in mucosal immunity. It is transported by transcytosis across mucosal epithelium by PIGR and secreted on the apical side in complex with PIGR secretory component to scan mucosal lining for pathogens. IgM-antigen complexes undergo FCMR-mediated retrotranscytosis across mucosal M cells toward antigen-presenting cells in mucosal lymphoid tissues. Isoform 2: Constant region of membrane-bound IgM, part of the B cell receptor complex (BCR). IgM BCR provides constitutive tonic signaling for B cell survival. Mediates pre-BCR signaling that regulates B cell selection and rearrangement of Ig genes via allelic exclusion. |
| Protein Name | Immunoglobulin Heavy Constant MuIg Mu Chain C RegionIg Mu Chain C Region BotIg Mu Chain C Region GalIg Mu Chain C Region Ou |
| Cellular Localisation | Isoform 1: SecretedDuring DifferentiationB-Lymphocytes Switch From Expression Of Membrane-Bound Igm To Secretion Of IgmIsoform 2: Cell MembraneSingle-Pass Membrane Protein |
| Alternative Antibody Names | Anti-Immunoglobulin Heavy Constant Mu antibodyAnti-Ig Mu Chain C Region antibodyAnti-Ig Mu Chain C Region Bot antibodyAnti-Ig Mu Chain C Region Gal antibodyAnti-Ig Mu Chain C Region Ou antibodyAnti-IGHM antibody |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org
12 months for antibodies. 6 months for ELISA Kits. Please see website T&Cs for further guidance