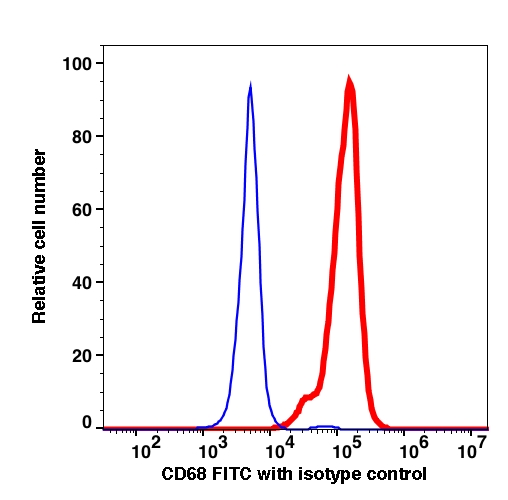
CD68 FITC
Catalog #
Size
| Conjugation | FITC |
|---|---|
| Antigen | CD68 |
| Clone | KP1 |
| Isotype | IgG1, k |
| Applications | FC |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Primary/Secondary | Primary |
| Storage | 2-8°C |
| Status | RUO |
| Excitation Laser | Blue (488nm) |
Description:
The clone KP1 recognizes 110 kDa highly glycosylated lysomal-associated membrane protein (LAMP) known as CD68. It plays important role in the immune process of endocytosis and/or lysosomal trafficking mostly carried out by cellular components of innate immunity. The CD68 is abundantly expressed in the cytoplasmic granules of macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils, basophils, subset of hematopoietic progenitors, γ/δ T cells, NK cells, LAK cells, subset of B cells, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. Studies suggest that KP1 is a very useful tool for studying disorders of the monocyte/macrophage system, including both reactive and neoplastic states.
The clone KP1 recognizes 110 kDa highly glycosylated lysomal-associated membrane protein (LAMP) known as CD68. It plays important role in the immune process of endocytosis and/or lysosomal trafficking mostly carried out by cellular components of innate immunity. The CD68 is abundantly expressed in the cytoplasmic granules of macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils, basophils, subset of hematopoietic progenitors, γ/δ T cells, NK cells, LAK cells, subset of B cells, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. Studies suggest that KP1 is a very useful tool for studying disorders of the monocyte/macrophage system, including both reactive and neoplastic states.