RpS27A Antibody
Katalog-Nummer OAED00135
Size : 50ug
Marke : Aviva Systems Biology
| Datasheets/Manuals | Printable datasheet for RpS27A Antibody (OAED00135) (OAED00135) |
|---|
| Predicted Species Reactivity | Bovine|Chicken|Dog|Drosophila|Fish|Guinea Pig|Hamster|Human|Monkey|Mouse|Porcine|Rabbit|Rat|Sheep|Xenopus|Yeast |
|---|---|
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Application | Immunocytochemistry|Western blot |
| Reconstitution and Storage | Long Term Storage : -20C |
| Immunogen | Native bovine Ubiquitin. |
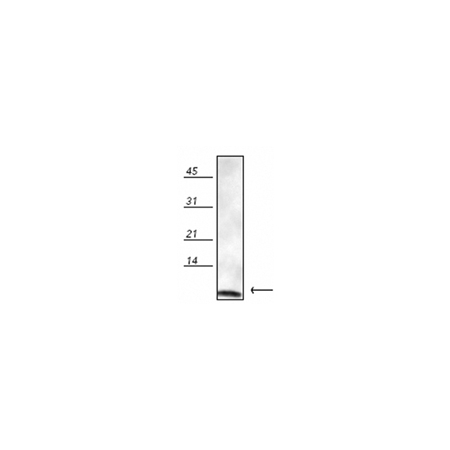
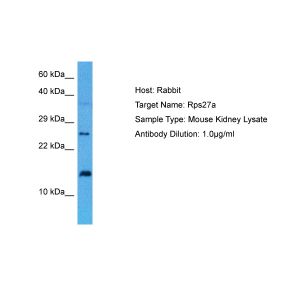
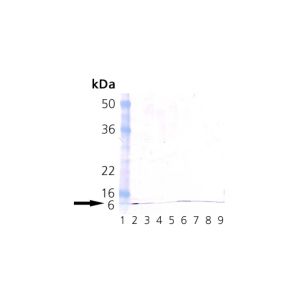
| Specificity | Recognizes human, mouse, rat, bovine, dog, chicken, Drosophila, fish, monkey, hamster, rabbit, guinea pig, pig, sheep, Xenopus and yeast Ubiquitin. Detects a band of ~8kDa by Western blot. |
| Formulation | Liquid. In PBS, pH 7.2, containing 50% glycerol and 0.09% sodium azide. |
| Purity | Protein A affinity purified. |
| Application Info | Immunocytochemistry Immunohistochemistry (paraffin sections) Western Blot (1:5000, ECL) Optimal conditions must be determined individually for each application. |
| Reference | SCA7 knockin mice model human SCA7 and reveal gradual accumulation of mutant ataxin-7 in neurons and abnormalities in short-term plasticity: H.Y. Zoghbi, et al. ; Neuron 37, 383 (2003), Application(s): ICC using mouse samples, Abstract; von Hippel-Lindau protein binds hyperphosphorylated large subunit of RNA polymerase II through a proline hydroxylation motif and targets it for ubiquitination: M.F. Czyzyk-Krzeska, et al. ; PNAS 100, 2706 (2003), Application(s): WB using rat samples, Abstract; p62 is a common component of cytoplasmic inclusions in protein aggregation diseases: H. Denk, et al. ; Am. J. Pathol. 160, 255 (2002), Application(s): IHC using mouse samples, Abstract; Phosphorylation of retinoid X receptor suppresses its ubiquitination in human hepatocellular carcinoma: Y. Okano, et al. ; Hepatology 35, 332 (2002), Application(s): WB using human samples, Abstract; HIV protease inhibitors protect apolipoprotein B from degradation by the proteasome: a potential mechanism for protease inhibitor-induced hyperlipidemia: S.L. Sturley, et al. ; Nat. Med. 7, 1327 (2001), Application(s): IP using human samples, Abstract; Impairment of bile salt-dependent lipase secretion in AR4-2J rat pancreatic cells induces its degradation by the proteasome: N. Bruneau, et al. ; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1530, 184 (2001), Application(s): WB using rat samples, Abstract; Activation-dependent degradation of protein kinase C eta: C.S. Hahn, et al. ; Oncogene 19, 4263 (2000), Application(s): WB using human samples, Abstract; The polyubiquitin gene is essential for meiosis in fission yeast: O. Niwa, et al. ; Exp. Cell Res. 254, 143 (2000), Application(s): WB using yeast samples, Abstract; Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits expression of CTP: phosphocholine cytidylyl transferase: S. Jackowski, et al. ; J. Biol. Chem. 275, 9699 (2000), Application(s): IP, WB using mouse samples, Abstract; Ubiquitination of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Env glycoprotein: J. Haas, et al. ; J. Virol. 74, 5373 (2000), Application(s): IP using mouse samples, Abstract; The degradation of apolipoprotein B100 is mediated by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and involves heat shock protein 70: H.N. Ginsberg, et al. ; J. Biol. Chem. 272, 20427 (1997), Application(s): IP using human samples, Abstract; |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | UBB |
| Gene Full Name | ubiquitin B |
| Alias Symbols | polyubiquitin;polyubiquitin-B. |
| NCBI Gene Id | 281370 |
| Protein Name | Polyubiquitin-B |
| Description of Target | Ubiquitin: Exists either covalently attached to another protein, or free (unanchored). When covalently bound, it is conjugated to target proteins via an isopeptide bond either as a monomer (monoubiquitin), a polymer linked via different Lys residues of the ubiquitin (polyubiquitin chains) or a linear polymer linked via the initiator Met of the ubiquitin (linear polyubiquitin chains). Polyubiquitin chains, when attached to a target protein, have different functions depending on the Lys residue of the ubiquitin that is linked: Lys-6-linked may be involved in DNA repair; Lys-11-linked is involved in ERAD (endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation) and in cell-cycle regulation; Lys-29-linked is involved in lysosomal degradation; Lys-33-linked is involved in kinase modification; Lys-48-linked is involved in protein degradation via the proteasome; Lys-63-linked is involved in endocytosis, DNA-damage responses as well as in signaling processes leading to activation of the transcription factor NF-kappa-B. Linear polymer chains formed via attachment by the initiator Met lead to cell signaling. Ubiquitin is usually conjugated to Lys residues of target proteins, however, in rare cases, conjugation to Cys or Ser residues has been observed. When polyubiquitin is free (unanchored-polyubiquitin), it also has distinct roles, such as in activation of protein kinases, and in signaling. |
| Uniprot ID | P0CG53 |
| Protein Accession # | NP_476778.1 |
| Nucleotide Accession # | NM_057430.4 |