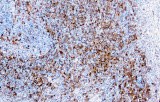
Anti-Fascin CE/IVD for IHC - Hematopathology
Fascin is an actin cross-linking protein and induces parallel actin bundles in cell protrusions and cell motility after the formation of lamellipodia or filopodia. Fascin is detectable in dendritic cells in normal and tumor tissues, Reed-Sternberg cells, nodular sclerosis variants, mixed cellularity, and lymphocyte depletion in Hodgkin's disease, while being undetectable in lymphoid cells, plasma cells, and myeloid cells. Anti-Fascin is useful for differentiating between Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. As Fascin is absent in neoplastic follicles in follicular lymphoma, Anti-Fascin is useful for differentiating these lymphomas from reactive follicular hyperplasia where the number of follicular dendritic cells are normal or increased.
Given its primary function in inducing membrane protrusions and increasing cell motility, in addition to serving as a marker for the identification of HL and dendritic tumors, overexpression of fascin has been shown to be correlated with disease progression in several types of human tumors including cancers of the lung, ovary, breast, pancreas, esophagus, stomach, colon, and skin.
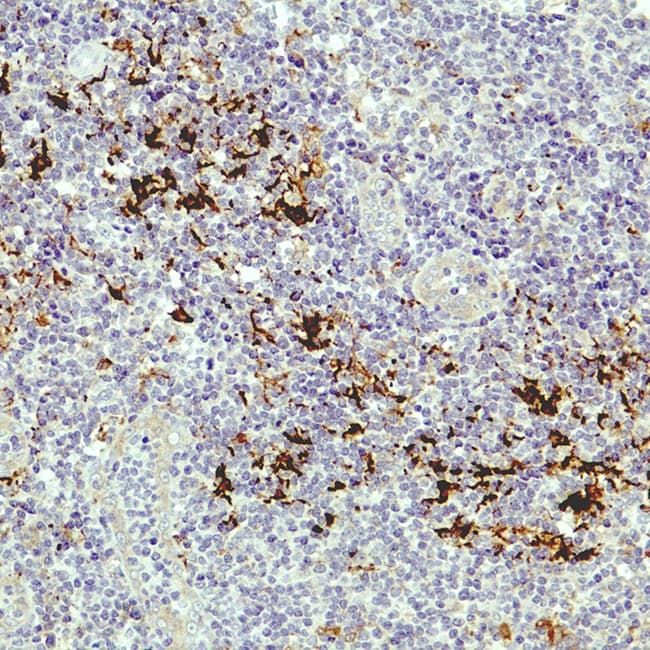

Tonsil section
Hodgkin's Lymphoma section
Search result : 6 product found
Refine your search :
RUOCE / IVD
- Unconjugated 6
- human 6
- mouse 6
- Primary antibody
- IHC 6
- 55k-2 6
Cat#
Description
Cond.
Price Bef. VAT
‹
›


