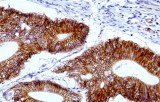
Anti-beta-catenin CE/IVD for IHC - Gastrointestinal pathology
Beta-catenin is a key regulatory protein involved in cell adhesion and signal transduction via the Wnt pathway. It plays an important role in development, cell proliferation and differentiation. Beta-catenin is part of a complex of proteins that constitute adherent junctions (AJ). AJs are necessary for the creation and maintenance of epithelial cell layers by regulating cell growth and cell adhesion. Beta-catenin also anchors the actin cytoskeleton and may be responsible for the transmission of the contact inhibition signal which causes the arrest of cell division when the epithelial sheet is terminated.
This protein binds to the product of the APC gene, which is mutated in adenomatous polyposis of the colon. Mutations in this protein are a cause of colorectal cancer (CRC), pilomatrixoma (PTR), medulloblastoma (MDB), and ovarian cancer. Mutations in the beta-catenin gene, CTNNB1, leading to the stabilization of beta-catenin in the cytoplasm and nuclear translocation, have been implicated in various tumor forms, including familial adenomatous polyposis, fibromatosis, Solitary fibrous tumors and carcinoma of the endometrium. Nuclear accumulation of beta-catenin in fibromatosis (desmoid tumor) at various sites, including the breast and mesentery, is useful for differentiating this tumor from other fibroblast-like lesions.


Colon cancer
Large intestine
Search result : 8 product found
Refine your search :
RUOCE / IVD
- Unconjugated 5
- human 5
- rabbit 5
- mouse 3
- Primary antibody
- IHC 8
- Polyclonal 5
- IHC516 3
Cat#
Description
Cond.
Price Bef. VAT
‹
›



