Cytometry conjugated CD antibodies
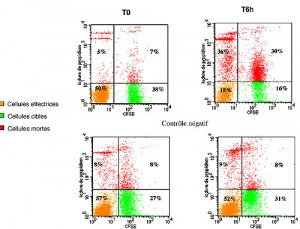
Cytometry conjugated CD antibodies are used in flow cytometry to detect antigens using fluorescent conjugated antibodies, each corresponding to a different protein in or on the cell surface. CD markers are especially useful for identification of leukocyte populations using flow cytometry. The HLDA (Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigens) workshop developed the CD nomenclature and has maintained the list of CD Markers ever since. Antibodies for use in mass cytometry are conjugated to single isotope heavy metal ions in the lanthanide series of elements.For instance, CD3 is expressed on T cells, CD19 on B cells, and CD14 on monocytes. By using antibodies conjugated with fluorophores, researchers can tag and analyze these CD antigens with high specificity and sensitivity.
Key Advantages:
- Multiparametric Analysis: Cytometry-conjugated CD antibodies allow for the simultaneous assessment of multiple CD antigens on individual immune cells. This multi-parameter analysis enables researchers to characterize complex immune cell populations in great detail.
- Cell Subset Identification: By targeting specific CD antigens, researchers can distinguish between various immune cell subtypes within a heterogeneous population, providing valuable insights into immune cell diversity and function.
- Functional Analysis: These antibodies can be used in conjunction with other functional assays to assess immune cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production, enhancing our understanding of immune responses.
- High Sensitivity: The fluorophore-conjugated antibodies offer high sensitivity, making it possible to detect rare immune cell populations or low-level antigen expression.
- Compatibility with Flow Cytometry: Cytometry-conjugated CD antibodies are compatible with flow cytometry, a widely used technique in immunology research, allowing for high-throughput analysis of immune cell populations.

