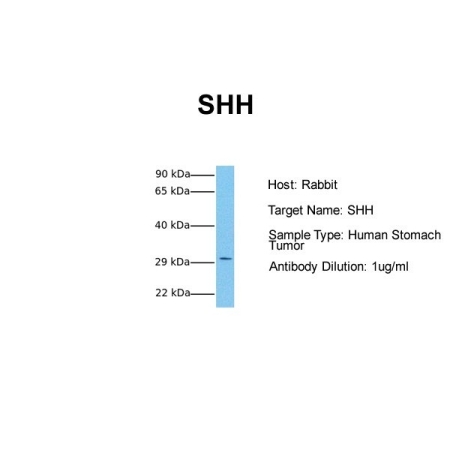
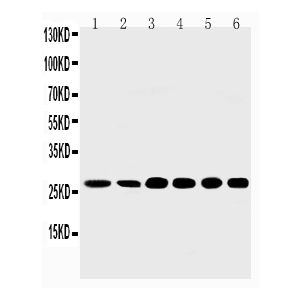
SHH Antibody - N-terminal region : HRP
Referencia ARP44235_P050-HRP
embalaje : 100ul
Marca : Aviva Systems Biology
| Datasheets/Manuals | Printable datasheet for anti-SHH (ARP44235_P050) antibody |
|---|
| Tested Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Chicken | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat, Cow, Dog, Goat, Guinea Pig, Horse, Rabbit, Zebrafish, Chicken | ||
| Product Format | Liquid. Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose. | ||
| Clonality | Polyclonal | ||
| Host | Rabbit | ||
| Application | IHC, WB | ||
| Reconstitution and Storage | For short term use, store at 2-8C up to 1 week. For long term storage, store at -20C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. | ||
| Immunogen | The immunogen is a synthetic peptide directed towards the N terminal region of human SHH | ||
| Purification | Affinity Purified | ||
| Predicted Homology Based on Immunogen Sequence | Cow: 93%; Dog: 100%; Goat: 93%; Guinea Pig: 100%; Horse: 100%; Human: 100%; Mouse: 100%; Rabbit: 100%; Rat: 100%; Zebrafish: 100% | ||
| Peptide Sequence | Synthetic peptide located within the following region: RCLLLVLVSSLLVCSGLACGPGRGFGKRRHPKKLTPLAYKQFIPNVAEKT | ||
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/ml | ||
| Blocking Peptide | For anti-SHH (ARP44235_P050) antibody is Catalog # AAP44235 (Previous Catalog # AAPP25615) | ||
| Enhanced Validation |
|
| Reference | Coon,D.R., (2006) Exp. Mol. Pathol. 80 (2), 119-123 |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | SHH |
| Gene Full Name | Sonic hedgehog |
| Alias Symbols | TPT, HHG1, HLP3, HPE3, SMMCI, ShhNC, TPTPS, MCOPCB5 |
| NCBI Gene Id | 6469 |
| Protein Name | Sonic hedgehog protein |
| Description of Target | SHH is a protein that is instrumental in patterning the early embryo. It has been implicated as the key inductive signal in patterning of the ventral neural tube, the anterior-posterior limb axis, and the ventral somites. Defects in this protein or in its signalling pathway are a cause of holoprosencephaly (HPE). It is also thought that mutations in its gene or in its signalling pathway may be responsible for VACTERL syndrome, which is characterized by vertebral defects, anal atresia, tracheoesophageal fistula with esophageal atresia, radial and renal dysplasia, cardiac anomalies, and limb abnormalities.This gene, which is expressed only during embryogenesis, encodes a protein that is instrumental in patterning the early embryo. It has been implicated as the key inductive signal in patterning of the ventral neural tube, the anterior-posterior limb axis, and the ventral somites. Of three human proteins showing sequence and functional similarity to the sonic hedgehog protein of Drosophila, this protein is the most similar. The protein is made as a precursor that is autocatalytically cleaved; the N-terminal portion is soluble and contains the signalling activity while the C-terminal portion is involved in precursor processing. More importantly, the C-terminal product covalently attaches a cholesterol moiety to the N-terminal product, restricting the N-terminal product to the cell surface and preventing it from freely diffusing throughout the developing embryo. Defects in this protein or in its signalling pathway are a cause of holoprosencephaly (HPE), a disorder in which the developing forebrain fails to correctly separate into right and left hemispheres. HPE is manifested by facial deformities. In addition, it is thought that mutations in this gene or in its signalling pathway may be responsible for VACTERL syndrome, which is characterized by vertebral defects, anal atresia, tracheoesophageal fistula with esophageal atresia, radial and renal dysplasia, cardiac anomalies, and limb abnormalities. |
| Uniprot ID | Q15465 |
| Protein Accession # | NP_000184 |
| Nucleotide Accession # | NM_000193 |
| Protein Size (# AA) | 462 |
| Molecular Weight | 28 kDa |
| Protein Interactions | UBC; SEL1L; DERL2; DERL1; SYVN1; HHIP; PTCH2; PTCH1; SHH; ADCYAP1; GAS1; |