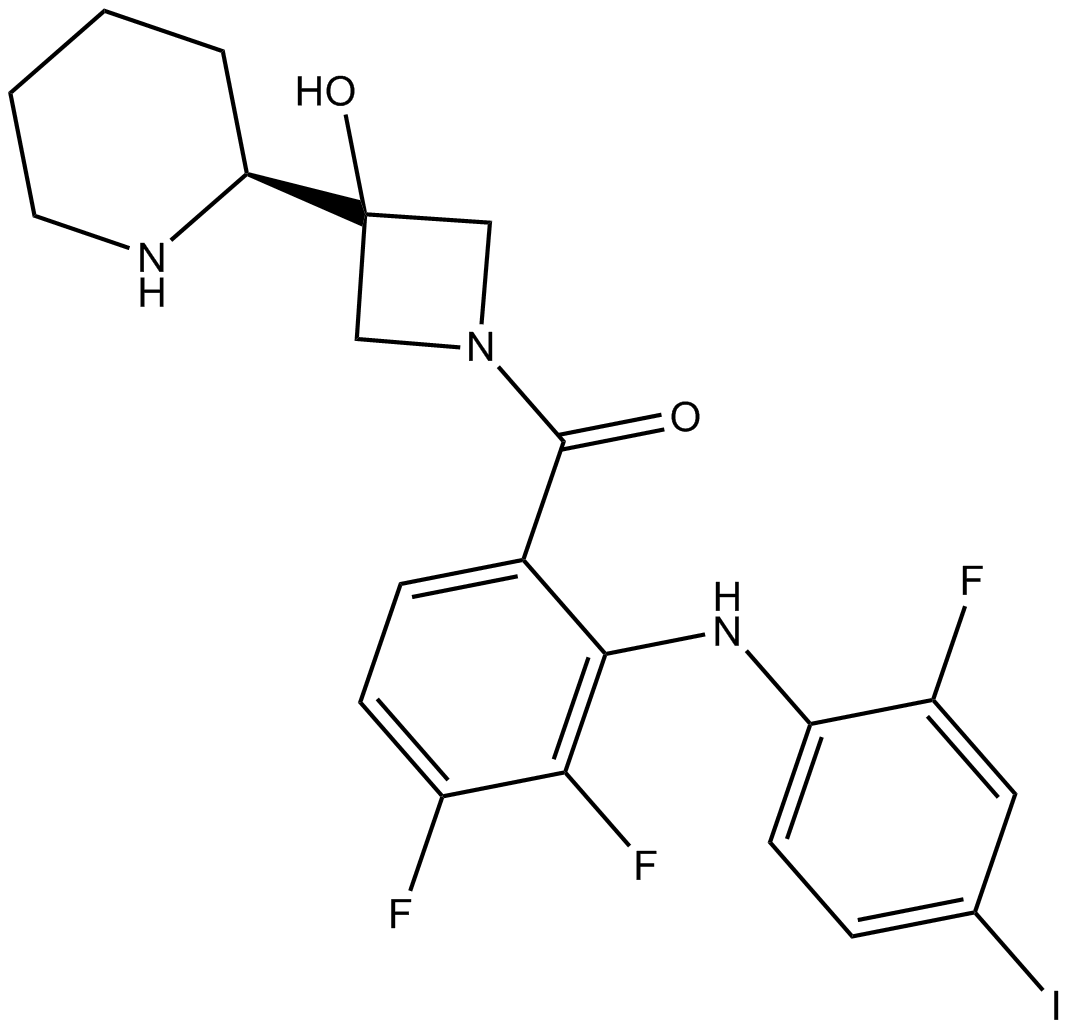
Cobimetinib [934660-93-2]
Marca : APExBIO Technology
Solicitar más información
Por favor, inicie sesión para usar esta función.
Cobimetinib
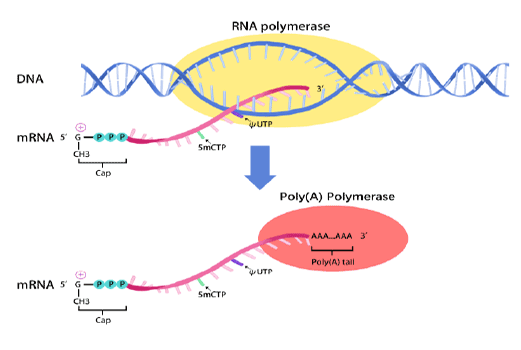
mRNA synthesis
In vitro transcription of capped mRNA with modified nucleotides and Poly(A) tail
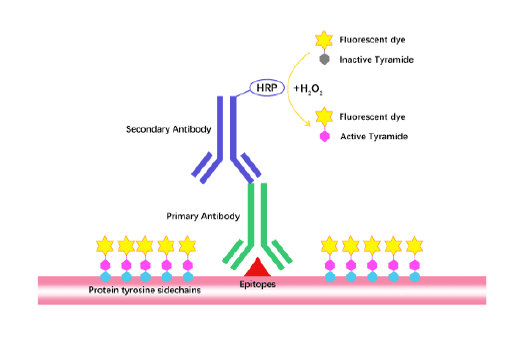
Tyramide Signal Amplification (TSA)
TSA (Tyramide Signal Amplification), used for signal amplification of ISH, IHC and IC etc.
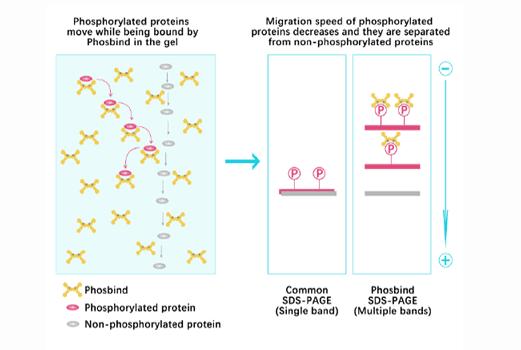
Phos Binding Reagent Acrylamide
Separation of phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated proteins without phospho-specific antibody
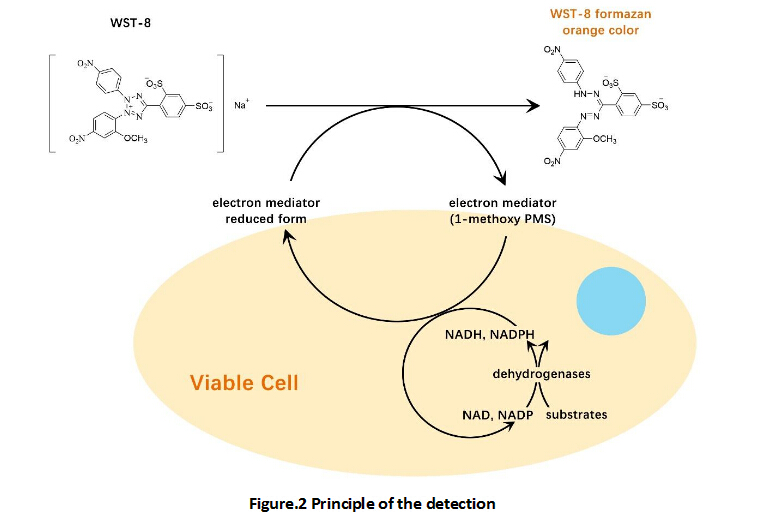
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
A convenient and sensitive way for cell proliferation assay and cytotoxicity assay
Inhibitor Cocktails
Protect the integrity of proteins from multiple proteases and phosphatases for different applications.
Background
Cobimetinib is a selective inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) with IC50 value of 0.9 nM [1].
MEK is a kinase enzyme which selectively phosphorylates Ser/Thr and Tyr residues and involved in the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways that play an important role in regulation of cell proliferation, survival, differentiation, motility and angiogenesis [2].
In a KRAS G13D and B-RAF G464V mutant MDA-MB-231T breast adenocarcinoma cells, Cobimetinib inhibited MEK with IC50 value of 0.2 nM [1]. In pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) model, Cobimetinib showed a sustained tumor pharmacodynamic response due to longer residence in tumor than in plasma [3].
In WM-266-4 xenograft mice, Cobimetinib decreased %pERK in tumor with IC50 values of 0.78 (WM-266-4) and 0.52 mM. Also, Cobimetinib (3.89 mM) increased IC50 value in WM-266-4 mice. In A375 xenograft mice, Cobimetinib (0.3-30 mg/kg) showed antitumor efficacy in a dose-dependent way. Cobimetinib is currently in phase I clinical trials as a potential antitumor agent [3].
References:
[1]. Rice KD, Aay N, Anand NK, et al. Novel Carboxamide-Based Allosteric MEK Inhibitors: Discovery and Optimization Efforts toward XL518 (GDC-0973). ACS Med Chem Lett, 2012, 3(5): 416-421.
[2]. Akinleye A, Furqan M, Mukhi N, et al. MEK and the inhibitors: from bench to bedside. J Hematol Oncol, 2013, 6: 27.
[3]. Wong H, Vernillet L, Peterson A, et al. Bridging the gap between preclinical and clinical studies using pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling: an analysis of GDC-0973, a MEK inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res, 2012, 18(11): 3090-3099.
Product Citation
- 1. Seoyul Lee, Wookyeom Yang, et al. "Inhibition of MEK-ERK pathway enhances oncolytic vaccinia virus replication in doxorubicin-resistant ovarian cancer." Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2022 Apr 18;25:211-224. PMID: 35592390
- 2. Julia C Gutjahr, Elisabeth Bayer, et al. "CD44 Engagement Enhances Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Adhesion To The Bone Marrow Microenvironment By Increasing VLA-4 Avidity." Haematologica. 2020 Jul 2; haematol.2019.231944. PMID: 32616529
- 3. White SM, Avantaggiati ML, et al. "YAP/TAZ Inhibition Induces Metabolic and Signaling Rewiring Resulting in Targetable Vulnerabilities in NF2-Deficient Tumor Cells." Dev Cell. 2019 May 6;49(3):425-443.e9. PMID: 31063758
- 4. Kulshrestha A, Katara GK, et al. "Targeting V-ATPase Isoform Restores Cisplatin Activity in Resistant Ovarian Cancer: Inhibition of Autophagy, Endosome Function, and ERK/MEK Pathway." J Oncol. 2019 Apr 1;2019:2343876. PMID: 31057611
- 5. Brunen D, de Vries RC, et al. "PIM Kinases Are a Potential Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Neuroblastoma." Mol Cancer Ther. 2018 Apr;17(4):849-857. PMID: 29440296
- 6. Gutjahr JC, Szenes E, et al. "Microenvironment-induced CD44v6 promotes early disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia." Blood. 2018 Mar 22;131(12):1337-1349. PMID: 29352038
Chemical Properties
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 531.31 |
| Cas No. | 934660-93-2 |
| Formula | C21H21F3IN3O2 |
| Synonyms | GDC-0973;XL-518;GDC 0973;XL 518;GDC0973;XL518 |
| Solubility | ≥26.55 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in H2O; ≥33.53 mg/mL in EtOH with gentle warming |
| Chemical Name | [3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)phenyl]-[3-hydroxy-3-[(2S)-piperidin-2-yl]azetidin-1-yl]methanone |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | C1CCNC(C1)C2(CN(C2)C(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3)F)F)NC4=C(C=C(C=C4)I)F)O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Protocol
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
| Cell lines | KRAS G13D and B-RAF G464V mutant MDA-MB-231T breast adenocarcinoma cell lines |
| Preparation method | The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >26.6 mg/mL. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
| Reacting condition | 0-10 nM |
| Applications | In the biochemical activity c-Raf/MEK1/ERK study, cobimetinib inhibited MEK1 activity with a IC50 value of 0.9 nM. Additionally, in MDA-MB-231T breast adenocarcinoma cells with KRAS G13D and B-RAF G464V mutant, cobimetinib was found to be able to inhibit MEK with the IC50 value of 0.2 nM. |
| Animal experiment [1]: | |
| Animal models | MDA-MB-231T mouse xenograft model |
| Dosage form | 0.3-30 mg/kg, oral, qd |
| Application | In an MDA-MB-231T efficacy study, cobimetinib demonstrated tumor growth inhibition values of 60 and 93% at 1 and 3 mg/kg, respectively, and statistically significant tumor regression was observed at higher doses. Overall, predicted ED50 and ED90 values were 0.6 and around 3 mg/kg/day, respectively, in the latter case corresponding to peak circulating plasma levels in the range of 130 nM. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: [1] Rice KD, Aay N, Anand NK, et al. Novel Carboxamide-Based Allosteric MEK Inhibitors: Discovery and Optimization Efforts toward XL518 (GDC-0973). ACS Med Chem Lett, 2012, 3(5): 416-421. | |




 COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
COA (Certificate Of Analysis)