TransGen Biotech
 |
||
TransGen Biotech, Inc. is a researcher, developer, manufacturer and distributor of more than 200 molecular and cellular biology products and kits for life science research and molecular diagnostics. In 2001, the company was founded by three scientists with a mission to produce innovative and cost-effective products for life science research. Currently, our products cover: plasmid based DNA markers, high efficiency chemically competent cells, 5 minutes PCR product cloning and expression vectors, a variety of PCR enzymes and supermix, RNase H deficient and high temperature RT enzymes, qPCR and qRT-PCR supermix, the highest efficiency mutagenesis kits, high quality nucleic acid extraction and purification kits, unstained and prestained protein markers, western blot markers, and protein purification resins, cell culture and transfection reagents, antibodies.
Website : www.transgenbiotech.com
| ||
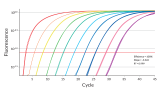
NGS Library quantification products
Accurate quantitation of the number of molecules in a library is the most critical step in the preparation steps for next-generation sequencing (NGS) to obtain high-quality reading data. Indeed, in order to obtain reliable and quality reading data, it is necessary to use a sufficient quantity of DNA, and in particular for Illumina® sequencing. The use of insufficient DNA will result in low sequencing efficiency and DNA overabundance will increase cluster density and result in poor quality data.
Standard methods of quantification of libraries for NGS, such as those based on electrophoresis or spectrophotometry, have low sensitivity, are not specific to the DNA bound to the adapter, and generally require a large amount of library samples for analysis. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) is considered to be the most accurate and efficient method of quantification of the library, providing consistency and reproducibility considerably higher than electrophoresis or spectrophotometry, which measure the total nucleic acid concentration. Amplification-based methods quantify only molecules that contain the two adapter sequences, thus providing a more accurate estimate of the concentration of the library molecules that can be sequenced.




