Application 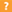
| FC, E, FTA |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P0DOX4 |
| Reactivity | Cynomolgus, Human, Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
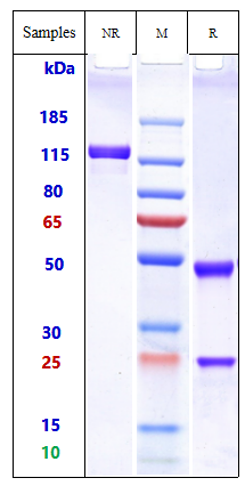
| Calculated MW | 146.46 KDa |
| Target/Specificity | IgE |
|---|---|
| Endotoxin | < 0.001EU/ µg,determined by LAL method. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Expression system | CHO Cell |
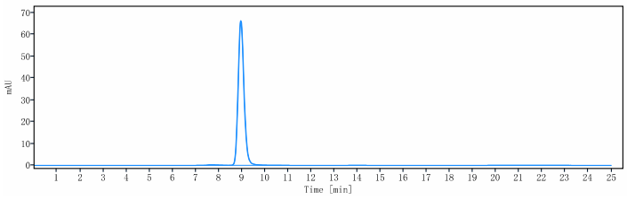
| Format | Purified monoclonal antibody supplied in PBS, pH6.0, without preservative.This antibody is purified through a protein A column. |
| Name | IGE |
|---|---|
| Function | Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, are membrane-bound or secreted glycoproteins produced by B lymphocytes. In the recognition phase of humoral immunity, the membrane-bound immunoglobulins serve as receptors which, upon binding of a specific antigen, trigger the clonal expansion and differentiation of B lymphocytes into immunoglobulins- secreting plasma cells. Secreted immunoglobulins mediate the effector phase of humoral immunity, which results in the elimination of bound antigens (PubMed:20176268, PubMed:22158414). The antigen binding site is formed by the variable domain of one heavy chain, together with that of its associated light chain. Thus, each immunoglobulin has two antigen binding sites with remarkable affinity for a particular antigen. The variable domains are assembled by a process called V-(D)-J rearrangement and can then be subjected to somatic hypermutations which, after exposure to antigen and selection, allow affinity maturation for a particular antigen (PubMed:17576170, PubMed:20176268). |
| Cellular Location | Secreted. Cell membrane |