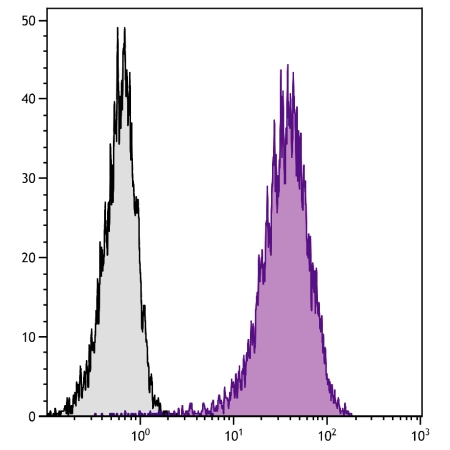
Human CD44 Antibody : FITC
Referentie OASB02575
Formaat : 25tests
Merk : Aviva Systems Biology
| Datasheets/Manuals | Printable datasheet for Human CD44 Antibody : FITC (OASB02575) |
|---|
| Tested Species Reactivity | Human |
|---|---|
| Predicted Species Reactivity | Human |
| Product Format | Liquid. Phosphate buffered saline containing 0.1% sodium azide |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Host | Mouse |
| Conjugation | FITC |
| Application | FC, ICC, IHC-F, IHC-P, WB |
| Additional Information | Description: CD44, also known as phagocytic glycoprotein-1 (Pgp-1), exists as a large number of different isoforms resulting from alternative RNA splicing. The major isoform expressed on lymphocytes, myeloid cells, and erythrocytes is a glycosylated type I transmembrane protein. Other variable isoforms containing glycosaminoglycans have molecular weights ranging from 110 to 250 kDa and are widely expressed on hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells. CD44 contributes to the adhesion of leukocytes to endothelial cells, stromal cells, and the extracellular matrix. It also plays a functional role in cell migration, lymphocyte homing, and adhesion during hematopoiesis and lymphocyte activation. |
| Reconstitution and Storage | Store at 2-8C |
| Immunogen | Purified human T cells |
| Concentration | Lot specific |
| Specificity | CD44 |
| Gene Symbol | CD44, CD44 |
|---|---|
| Gene Full Name | CD44 molecule (Indian blood group) |
| Alias Symbols | IN, LHR, MC56, MDU2, MDU3, MIC4, Pgp1, CDW44, CSPG8, HCELL, HUTCH-I, ECMR-III |
| NCBI Gene Id | 960; 105717277 |
| Protein Name | CD44 antigen |
| Description of Target | The protein encoded by this gene is a cell-surface glycoprotein involved in cell-cell interactions, cell adhesion and migration. It is a receptor for hyaluronic acid (HA) and can also interact with other ligands, such as osteopontin, collagens, and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). This protein participates in a wide variety of cellular functions including lymphocyte activation, recirculation and homing, hematopoiesis, and tumor metastasis. Transcripts for this gene undergo complex alternative splicing that results in many functionally distinct isoforms, however, the full length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. Alternative splicing is the basis for the structural and functional diversity of this protein, and may be related to tumor metastasis. |
| Uniprot ID | P16070, A0A2K5DU87 |
| Protein Accession # | NP_000601.3 |
| Nucleotide Accession # | NM_000610.3 |