Aptamer synthesis
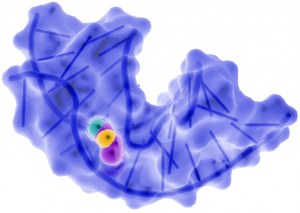
Aptamers are nucleic acids that bind with high specificity and high affinity to a target. The targets can be of various types : proteins, peptides, nucleic acids, toxins, viral particles... They can be considered as putative ligands for any molecule and can be used in basic research, in analysis tools, as sensors, and also as therapeutic tools. As aptamers are nucleic acids, there is no problem of reproducibility during their production compared to antibodies.
For your projects involving aptamer selection, identification, labeling and optimization, please contact us.
Aptamers, an alternative to antibodies
Advantages:
- Chemically synthesized: cheap and easy to produce
- No organisms involved: GMP easy
- Low/non-immunogenic targets can be addressed
- Can be selected under non-physiologic conditions
- Easily modified for chemical conjugation, labeling, other properties
- Small size: good transport, more moles/gram
- Stable: no cold chain required
What are Aptamers ?
Aptamers are single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules that can bind to pre-selected targets including proteins and peptides with high affinity and specificity
These molecules can assume a variety of shapes due to their propensity to form helices and single-stranded loops, explaining their versatility in binding to diverse targets.
Contrary to the actual genetic material, their specificity and characteristics are not directly determined by their primary sequence, but instead by their tertiary structure.
Comparison Aptamers / Antibodies:
Applications:
- Biosensors and novel assays
- Lateral flow assays
- Western blotting
- ELISA/ELONA
- Flow cytometry
- Therapeutics and drug delivery including siRNA



