Mouse anti Cytokeratin 14 / Keratin K14
Référence MUB0323P
Conditionnement : 0.1mg
Marque : Nordic Mubio
| Clone | RCK107 |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Product Type | Monoclonal Antibody Primary Antibodies |
| Units | 0.1 mg |
| Host | Mouse |
| Species Reactivity | Canine Human Mouse Rat Swine |
| Application | Flow Cytometry Immunocytochemistry Immunohistochemistry (frozen) Western Blotting |
Background
Cytokeratins are a subfamily of intermediate filament proteins and are characterized by a remarkable biochemical diversity, represented in Human epithelial tissues by at least 20 different polypeptides. They range in molecular weight between 40 kDa and 68 kDa and isoelectric pH between 4.9 – 7.8. The individual Human Cytokeratins are numbered 1 to 20. The various epithelia in the Human body usually express Cytokeratins which are not only characteristic of the type of epithelium, but also related to the degree of matuRation or differentiation within an epithelium. Cytokeratin subtype expression patterns are used to an increasing extent in the distinction of different types of epithelial malignancies. The Cytokeratin antibodies are not only of assistance in the differential diagnosis of tumors using immunohistochemistry on tissue sections, but are also a useful tool in cytopathology and flow cytometric assays.
Source
RCK107 is a Mouse monoclonal IgG1 antibody derived by fusion of SP2/0-Ag14 Mouse myeloma cells with spleen cells from a Mouse immunized with a cytoskeletal preparation of TR146 epithelial cells.
Product
Each vial contains 100 ul 1 mg/ml purified monoclonal antibody in PBS containing 0.09% sodium azide.
Formulation: Each vial contains 100 ul 1 mg/ml purified monoclonal antibody in PBS containing 0.09% sodium azide.
Specificity
RCK107 reacts exclusively with Cytokeratin 14 which is present in basal cell compartments of stRatified and combined epithelia.
Applications
RCK107 is suitable for immunocytochemistry, immunohistochemistry on frozen sections, flow cytometry and immunoblotting. Optimal antibody dilution should be determined by titration; recommended range is 1:100 – 1:200 for flow cytometry, and for immunohistochemistry with avidin-biotinylated Horseradish peroxidase complex (ABC) as detection reagent, and 1:100 – 1:1000 for immunoblotting applications.
Storage
The antibody is shipped at ambient temperature and may be stored at +4°C. For prolonged storage prepare appropriate aliquots and store at or below -20°C. Prior to use, an aliquot is thawed slowly in the dark at ambient temperature, spun down again and used to prepare working dilutions by adding sterile phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.2). Repeated thawing and freezing should be avoided. Working dilutions should be stored at +4°C, not refrozen, and preferably used the same day. If a slight precipitation occurs upon storage, this should be removed by centrifugation. It will not affect the performance or the concentration of the product.
Caution
This product is intended FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY, and FOR TESTS IN VITRO, not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures involving humans or animals. It may contain hazardous ingredients. Please refer to the Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for additional information and proper handling procedures. Dispose product remainders according to local regulations.This datasheet is as accurate as reasonably achievable, but Nordic-MUbio accepts no liability for any inaccuracies or omissions in this information.
References
1. Wetzels, R. H., Kuijpers, H. J., Lane, E. B., Leigh, I. M., Troyanovsky, S. M., Holland, R., van Haelst, U. J., and Ramaekers, F. C. (1991). Basal cell-specific and hyperproliferation-related Keratins in Human breast cancer, Am J Pathol 138, 751-63. 2. Smedts, F., Ramaekers, F., Troyanovsky, S., Pruszczynski, M., Robben, H., Lane, B., Leigh, I., Plantema, F., and Vooijs, P. (1992). Basal-cell Keratins in cervical reserve cells and a comparison to their expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, Am J Pathol 140, 601-12. 3. Wetzels, R. H., Schaafsma, H. E., Leigh, I. M., Lane, E. B., Troyanovsky, S. M., Wagenaar, S. S., Vooijs, G. P., and Ramaekers, F. C. (1992). Laminin and type VII collagen distribution in different types of Human lung carcinoma: correlation with expression of Keratins 14, 16, 17 and 18, Histopathology 20, 295-303. 4. Bauwens, L. J., De Groot, J. C., Ramaekers, F. C., Veldman, J. E., and Huizing, E. H. (1992). Expression of intermediate filament proteins in the adult Human vestibular labyrinth, Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 101, 479-86. 5. Smedts, F., Ramaekers, F., Troyanovsky, S., Pruszczynski, M., Link, M., Lane, B., Leigh, I., Schijf, C., and Vooijs, P. (1992). Keratin expression in cervical cancer, Am J Pathol 141, 497-511. 6. Vos, J. H., van den Ingh, T. S., de Neijs, M., van Mil, F. N., Ivanyi, D., and Ramaekers, F. C. (1992). Immunohistochemistry with Keratin monoclonal antibodies in canine tissues: urogenital tract, respiratory tract, (neuro-)endocrine tissues, choroid plexus and spinal cord, J Vet Med 39, 721-40. 7. Vos, J. H., van den Ingh, T. S., Ramaekers, F. C., Molenbeek, R. F., de Neijs, M., van Mil, F. N., and Ivanyi, D. (1993). The expression of Keratins, vimentin, neurofilament proteins, smooth muscle actin, neuron-specific enolase, and synaptophysin in tumors of the specific glands in the canine anal region, Vet Pathol 30, 352-61. 8. van Leenders, G., Dijkman, H., Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C., Ruiter, D., and Schalken, J. (2000). Demonstration of intermediate cells during Human prostate epithelial differentiation in situ and in vitro using triple-staining confocal scanning microscopy, Lab Invest 80, 1251-8. 9.Spies I. Immunolocation of mitochondria-rich cells in epidermis of the common toad, Bufo bufo L. (1997) Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 118,285-91. 10. Smalley MJ, Titley J, O'Hare MJ. Clonal characterization of mouse mammary luminal epithelial and myoepithelial cells separated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1998 Oct;34(9)711-21. doi 10.1007s11626-998-0067-0.
Protein Reference(s)
Database Name: UniProt
Accession Number: P02533
Safety Datasheet(s) for this product:
 NM_Sodium Azide NM_Sodium Azide |

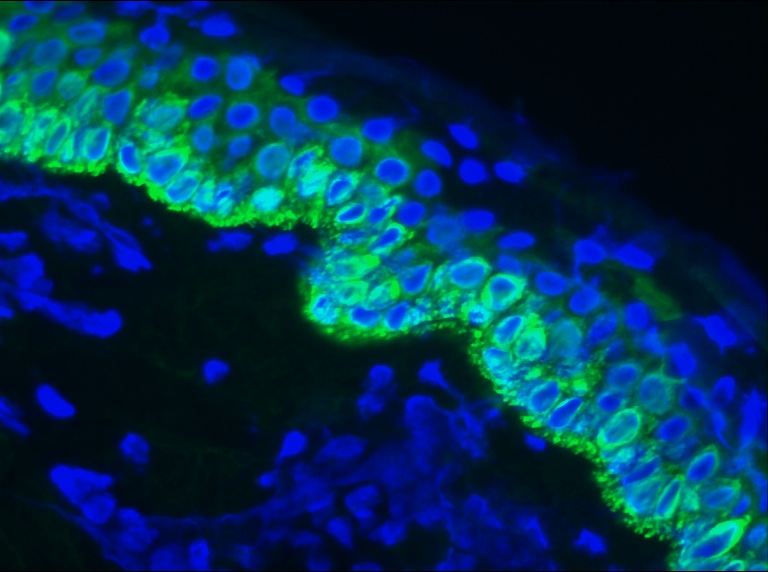
Figure 1. Indirect immunofluorescence staining of swine skin frozen tissue section with MUB0323P (RCK107; Mouse anti keratin 14). Dilution 1:200. Specific staining of the basal and parabasal cells of the epidermis. No reactivity in the connective tissues.