Cholesterol [57-88-5]
Referência sc-202539C
Tamanho : 5g
Marca : Santa Cruz Biotechnology
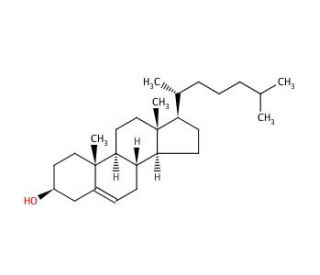
Cholesterol (CAS 57-88-5)
ACCÈS RAPIDE AUX LIENS
Le cholestérol est un lipide qui constitue environ 20 à 25 % des composants structurels des membranes cellulaires. Il détermine la fluidité et la perméabilité de la membrane, la rendant perméable à l'eau mais pas aux ions et aux protons. Le cholestérol régule également les fonctions des transporteurs et des protéines de signalisation présents sur la membrane plasmique. Le cholestérol peut être utilisé dans les préparations de liposomes.
Cholesterol (CAS 57-88-5) Références:
- Cholestérol, maladie d'Alzheimer, maladies à prions: un ménage à trois ? | Pani, A., et al. 2010. Curr Drug Targets. 11: 1018-31. PMID: 20450474
- Implications physiologiques et pathologiques du cholestérol. | Cortes, VA., et al. 2014. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 19: 416-28. PMID: 24389193
- Sur la distribution déroutante du cholestérol dans la membrane plasmique. | Giang, H. and Schick, M. 2016. Chem Phys Lipids. 199: 35-38. PMID: 26724709
- Caractéristiques structurelles communes des sites de liaison du cholestérol dans les protéines solubles cristallisées. | Bukiya, AN. and Dopico, AM. 2017. J Lipid Res. 58: 1044-1054. PMID: 28420706
- Mesure des forces d'une seule molécule dans les complexes hôte-guest de cholestérol et de cyclodextrine. | Pandey, S., et al. 2021. J Phys Chem B. 125: 11112-11121. PMID: 34523939
- Le site d'oxydation du cholestérol a un impact sur sa localisation et la formation de domaines dans la membrane plasmique neuronale. | Wilson, KA., et al. 2021. ACS Chem Neurosci. 12: 3873-3884. PMID: 34633798
- Synthèse et évaluation biologique d'analogues cationiques du cholestérol TopFluor. | Jurášek, M., et al. 2021. Bioorg Chem. 117: 105410. PMID: 34700109
- Profils de cholestérol et de glucose en fonction de différents niveaux de peptide C à jeun: une analyse transversale dans une cohorte saine de la République tchèque. | Kron, V., et al. 2021. J Appl Biomed. 19: 220-227. PMID: 34907741
- Effets du régime cétogène sur les fonctions cognitives de souris nourries avec un régime riche en graisses et en cholestérol. | Lin, DT., et al. 2022. J Nutr Biochem. 104: 108974. PMID: 35196576
- Effets du cholestérol sur le mécanisme de la fengycine, un biofongicide. | Sur, S. and Grossfield, A. 2022. Biophys J. 121: 1963-1974. PMID: 35422413
- Effets du cholestérol et du PIP2 sur les interactions entre la glycophorine A et la bande 3 dans les bicouches lipidiques. | Qin, X., et al. 2022. Biophys J. 121: 2069-2077. PMID: 35524411
- La quantité de cholestérol membranaire nécessaire à l'adhésion et à la prolifération des cellules en l'absence de sérum. | Takii, S., et al. 2022. PLoS One. 17: e0259482. PMID: 35857759
- Quantification absolue du cholestérol à partir de coupes de tissus minces par imagerie de spectrométrie de masse par désorption laser assistée par l'argent. | Nezhad, ZS., et al. 2022. Anal Bioanal Chem. 414: 6947-6954. PMID: 35953724
Cholesterol (57-88-5) Cibles de modulation
Apparence :
Crystalline powder
État Physique :
Solid
Solubilité :
Soluble in hot alcohol, chloroform, pyridine, benzene, fats , oils, acetone, dioxane, ethyl acetate, petroleum ether, and ether. Insoluble in water.
Stockage :
Store at -20° C
Point de fusion :
147-149° C
Point d'Ébullition :
360° C
Densité :
1.07 g/cm3 at 25° C
Indice de Réfraction :
n20D 1.53 (Predicted)
Activité Optique :
α20D -36, c = 2 in dioxane
IC50 :
CEM : IC50 = >50 µM (human); MCF7 : IC50 = >50 µM (human); BJ: IC50 = >50 µM (human); HT-29 : IC50 = >50 µM (human)
WGK Allemagne :
1
RTECS :
FZ8400000
PubChem CID :
5997Indice Merck :
14: 2201
Numéro MDL :
MFCD00003646
Numéro EC :
200-353-2
Registre Beilstein :
1915888
SMILES :
C[C@H](CCCC(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@@H]2[C@@]1(CC[C@H]3[C@H]2CC=C4[C@@]3(CC[C@@H](C4)O)C)C
Télécharger la Fiche de Sécurité/ SDS (MSDS)
Région
EXEMPLE de Certificat d'Analyse (CoA)
Cholesterol | CAS 57-88-5 SAMPLE Certificate of AnalysisCERTIFICAT D'ANALYSE
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de Lot
SAMPLE Certificate of Analysis (COA)
| Test | Specification | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Fine white crystalline powder | |
| Identification | Complies | |
| Purity | 99% | |
| Melting Point | 147.5°C | |
| Residue on Ignition | < 0.1% | |
| Solubility | Alcohol | Complies |
| Specific Rotation | -37° | |
| Loss on Drying | < 0.1% |
Comment demander un certificat d'analyse (COA) lorsqu'il n'est pas disponible en ligne ?
Si vous avez besoin d'un certificat d'analyse (COA) et que vous ne pouvez pas le trouver sur le site web, il existe une procédure simple pour en obtenir un. Voici comment procéder.
- Vérifiez le plan du site avant de faire une demande pour vous assurer que vous avez recherché dans toutes les zones disponibles où les COA peuvent être répertoriés.
- Si votre recherche initiale n'est pas fructueuse, la prochaine étape consiste à demander de l'aide. Vous pouvez contacter le service client par e-mail, téléphone ou parfois via une fonctionnalité de chat en direct.
- Il vous suffit de soumettre une demande. Lorsque vous contactez le service client, vous devrez fournir le nom du produit, le numéro de lot et vos coordonnées. Indiquez explicitement que vous demandez le COA pour votre article spécifique.
- N'oubliez pas de faire un suivi. Si vous ne recevez pas de réponse dans un délai raisonnable, n'hésitez pas à relancer et assurez-vous de conserver un enregistrement de vos communications.
Suivez ces étapes pour obtenir le COA dont vous avez besoin, même s'il n'est pas disponible en ligne.
Informations pour la commande
| Nom du produit | Ref. Catalogue | COND. | Prix HT | QTÉ | Favoris | |
Cholesterol, 5 g | sc-202539C | 5 g | .00 | |||
Cholesterol, 25 g | sc-202539 | 25 g | .00 | |||
Cholesterol, 100 g | sc-202539A | 100 g | .00 | |||
Cholesterol, 250 g | sc-202539B | 250 g | .00 | |||
Cholesterol, 1 kg | sc-202539D | 1 kg | .00 | |||
Cholesterol, 5 kg | sc-202539E | 5 kg | 4.00 |



